Vault Doors: A Comprehensive Guide to Security and Design
Vault doors represent the pinnacle of security, designed to protect valuable assets and sensitive information. These massive barriers, often associated with banks and high-security facilities, have a rich history and continue to evolve with advancements in technology and evolving security threats. This comprehensive guide explores the history, design, functionality, and modern applications of vault doors.
A Brief History of Vault Doors
The concept of securing valuables dates back to ancient civilizations, with rudimentary locks and fortified chambers serving as early precursors to vault doors. However, the modern vault door emerged in the mid-19th century, driven by the growth of banking and the need for enhanced security against increasingly sophisticated criminals. Early vault doors were primarily made of thick steel and relied on complex mechanical locking mechanisms.
The invention of the time lock in the late 19th century revolutionized vault security. Time locks prevented vault doors from being opened until a pre-set time, even if the correct combination was known. This innovation significantly reduced the risk of robbery by forcing criminals to wait, increasing their chances of apprehension. Over time, these mechanisms became more sophisticated, incorporating multiple time locks to further enhance security.
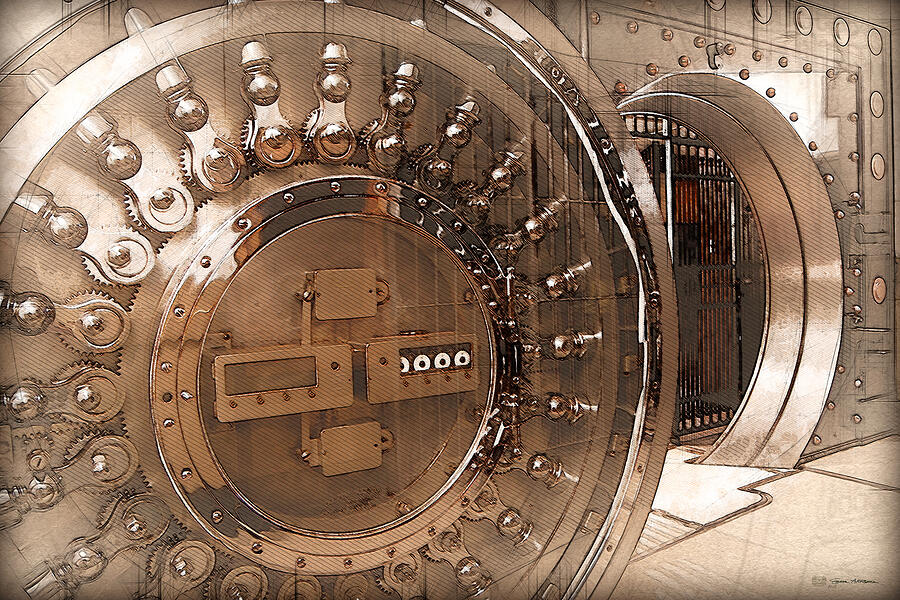
Design and Construction
Modern vault doors are engineering marvels, incorporating multiple layers of defense to withstand various forms of attack. The door itself is typically constructed from multiple layers of steel, often incorporating hardened steel alloys and composite materials. These materials provide resistance against drilling, cutting, explosives, and other forms of forced entry. The thickness of the door varies depending on the level of security required, ranging from several inches to several feet.
Locking Mechanisms
The locking mechanisms of vault doors are equally complex, utilizing a combination of mechanical and electronic components. Traditional combination locks remain a staple, offering a high degree of security when properly maintained. However, electronic locks are becoming increasingly popular, offering features such as audit trails, remote access control, and biometric authentication. Many vault doors incorporate multiple locking systems to provide redundancy and enhance security. [See also: High-Security Lock Systems]
Boltwork
The boltwork is the system of interlocking bolts that secure the vault door to the frame. These bolts are typically made of hardened steel and extend deep into the surrounding walls, providing a formidable barrier against forced entry. The number and size of the bolts vary depending on the size and security level of the vault. Some vault doors also incorporate relocking devices, which automatically activate if the door is tampered with or attacked.
Frame and Installation
The frame of a vault door is as important as the door itself. It must be securely anchored to the surrounding walls to prevent criminals from simply bypassing the door by attacking the frame. The frame is typically made of reinforced concrete or steel and is designed to withstand significant force. Proper installation is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the vault door, and it should only be performed by experienced professionals.
Functionality and Security Levels
Vault doors are designed to provide varying levels of security, depending on the specific needs of the application. The level of security is typically determined by the amount of time and resources required to breach the door. The Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is a leading organization that tests and certifies vault doors based on their resistance to various forms of attack.
UL Ratings
UL ratings for vault doors range from Class M to Class 3, with Class 3 offering the highest level of security. Each class corresponds to a specific amount of time and types of tools required to penetrate the door. For example, a Class M vault door is designed to resist entry for 15 minutes using common hand tools, while a Class 3 vault door is designed to resist entry for 60 minutes using sophisticated power tools and torches.
Beyond UL Ratings
In addition to UL ratings, some vault doors are also tested and certified to other standards, such as those developed by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). These standards may include tests for resistance to explosives, firearms, and other specialized threats. The specific security requirements for a vault door will depend on the value of the assets being protected and the perceived level of risk.
Modern Applications of Vault Doors
While vault doors are most commonly associated with banks and financial institutions, they are also used in a variety of other applications, including:
- Museums and Art Galleries: To protect valuable artifacts and artwork.
- Government Facilities: To secure sensitive documents and equipment.
- Pharmaceutical Companies: To safeguard controlled substances and research data.
- Data Centers: To protect servers and sensitive information from physical theft or damage.
- Private Residences: High net worth individuals may install vault doors to protect valuables and create secure rooms.
The use of vault doors in private residences is a growing trend, driven by increasing concerns about security and privacy. These residential vault doors are often customized to blend seamlessly with the surrounding décor, providing a discreet yet effective layer of protection.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements continue to shape the design and functionality of vault doors. Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint and iris scanning, is becoming increasingly common, providing a higher level of security and convenience. Smart vault doors can be integrated with alarm systems and surveillance cameras, providing real-time monitoring and alerts. [See also: The Future of Biometric Security]
The use of advanced materials, such as composite materials and high-strength alloys, is also improving the performance of vault doors. These materials offer superior resistance to various forms of attack while reducing the overall weight of the door. This makes installation easier and reduces the stress on the surrounding structure.
Choosing the Right Vault Door
Selecting the right vault door requires careful consideration of several factors, including the level of security required, the size and layout of the space, and the budget. It is essential to work with a reputable security professional who can assess your specific needs and recommend the appropriate vault door. Factors to consider include:
- Security Rating: Choose a vault door with a UL rating that meets your specific security requirements.
- Size and Weight: Ensure that the vault door is appropriately sized for the opening and that the surrounding structure can support its weight.
- Locking Mechanism: Select a locking mechanism that provides the desired level of security and convenience.
- Installation: Ensure that the vault door is installed by experienced professionals to ensure its effectiveness.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the continued performance of the vault door.
The Future of Vault Doors
The future of vault doors will likely be driven by continued advancements in technology and evolving security threats. We can expect to see increased integration of biometric authentication, smart technology, and advanced materials. The development of new testing standards and certifications will also play a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness of vault doors.
As technology advances, so do the methods used to compromise security. Therefore, ongoing research and development are essential to stay ahead of potential threats and ensure the continued effectiveness of vault doors. The ongoing evolution of vault doors ensures that they remain the gold standard in physical security, protecting valuable assets and sensitive information for years to come. The best vault doors are constantly being improved upon.
Conclusion
Vault doors represent the ultimate in physical security, providing a formidable barrier against theft, vandalism, and other threats. With a rich history and ongoing advancements in technology, vault doors continue to play a vital role in protecting valuable assets and sensitive information in a wide range of applications. From banks and museums to private residences, vault doors offer peace of mind and security in an increasingly uncertain world. Investing in a high-quality vault door is a worthwhile investment in the protection of your valuables and peace of mind.
